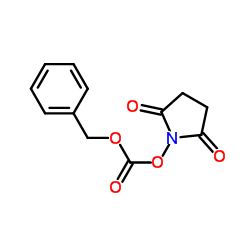
Benzyloxycarbonylsuccinimide
Nanjing Finechem Holdings Co., LTD
Synonyms
N-(Benzyloxycarbonyloxy)-succinimide
Benzyl N-succinimidyl carbonate
N-Carbobenzoxyoxysuccinimide
1-{[(Benzyloxy)carbonyl]oxy}-2,5-pyrrolidinedione
O-Cbz-N-hydroxysuccinimide
EINECS 236-075-3
1-{[(Benzyloxy)carbonyl]oxy}pyrrolidine-2,5-dione
2,5-Pyrrolidinedione, 1-(((phenylmethoxy)carbonyl)oxy)-
1-{[(Benzyloxy)carbonyl]oxy}pyrrolidin-2,5-dion
Nα-(Benzyloxycarbonyloxy) Succinimide
Product Description
Benzyloxycarbonylsuccinimide (abbreviated as Z-NSu) is an important amino acid derivative and a widely
used amino acid protecting reagent in organic synthesis. Z-NSu is produced by the reaction of
N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) with benzyl chloroformate, which results in the formation of the active ester
Z-NSu.
Z-NSu is used as a protective group for the amino function of Lysine, Arginine, and Histidine in peptide
synthesis. It has also found applications in the selective modification of peptides, such as labeling
and crosslinking, and as a reagent for the synthesis of unnatural amino acids.
The use of Z-NSu has become increasingly popular in the pharmaceutical industry due to its ability to
facilitate peptide synthesis and improve peptide stability. The global peptide synthesis market has been
growing at a steady pace in recent years, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5%
from 2021 to 2028. This growth is mainly driven by the increasing demand for peptides in therapeutic
applications and the development of new peptide-based drugs.
In addition to its use in peptide synthesis, Z-NSu has also been applied in the field of bioconjugation,
where it is used as a crosslinking reagent to link biomolecules such as proteins and peptides. The
global bioconjugation market is expected to reach USD 16.5 billion by 2025, driven by the growing demand
for bioconjugates in drug delivery, diagnostics, and imaging.
Despite its widespread use, Z-NSu has been associated with some drawbacks, including low solubility in
water, which can lead to low yields and incomplete reactions. Alternative protecting reagents, such as
Fmoc, Boc, and t-Boc, have been developed to overcome these limitations.
In conclusion, Z-NSu is a versatile amino acid protecting reagent with broad applications in peptide
synthesis and bioconjugation. Its increasing use in the pharmaceutical industry and the growing demand
for peptides and bioconjugates are expected to drive the market growth in the coming years. However, its
limitations in solubility call for the development of alternative protecting reagents that can address
these challenges.