
| N/A |
| Packing | |
|---|---|
| Storage | Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years;In solvent -80°C 6 months, -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping | Room temperature in continental US; may vary elsewhere |
Tel: 0086-25-52397805
Email: sales7@alchemist-chem.com

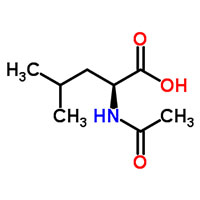
| Common Names | N-Acetyl-L-leucine | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure |  |
||
| CAS No. | 1188-21-2 | Boiling Point (℃) | 369.6±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Weight | 173.21 | Melting Point (℃) | 187-190 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Vapor Specific Gravity | N/A |
| Molecular Formula | C8H15NO3 | Flash Point (℃) | 177.4±23.2 °C |
| Solubility | 0.81 g/100 mL (20 | ||