
| N/A |
| Packing | |
|---|---|
| Storage | Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years;In solvent -80°C 6 months, -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping | Room temperature in continental US; may vary elsewhere |
Tel: 0086-25-52397805
Email: sales7@alchemist-chem.com

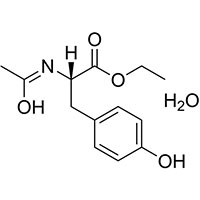
| Common Names | Ethyl N-acetyl-L-tyrosinate hydrate (1:1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure |  |
||
| CAS No. | 36546-50-6 | Boiling Point (℃) | 464.4±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Weight | 251.278 | Melting Point (℃) | 80-81 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Vapor Specific Gravity | N/A |
| Molecular Formula | C13H17NO4 | Flash Point (℃) | 234.6±25.9 °C |
| Solubility | N/A | Autoignition Temperature (℃) | N/A |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | T+:Very toxic | ||
| Safety Phrases | S1-S28-S45 | ||
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport | ||
| WGK Germany |