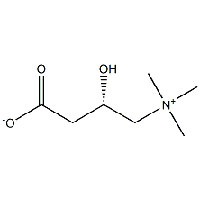
Synonyms
L-(-)-Carnitine
karnitin
ST 198
EINECS 208-768-0
3-Carboxy-2-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethyl-1-propanaminium Hydroxide Inner Salt
Carnitrine
USPorFCC
(R)-Carnitine
Ammonium, (3-carboxy-2-hydroxypropyl)trimethyl-, hydroxide, inner salt, L-
L-CARNITIN
3-Hydroxy-4-(trimethylammonio)butanoate
g-Trimethylammonium-b-hydroxybutirate
CAR-OH
Product Description
L-Carnitine is a naturally occurring amino acid that plays a critical role in energy metabolism. It is
involved in the transport of fatty acids into the mitochondria, where they are oxidized to produce
energy. L-Carnitine is produced in the human body from the amino acids lysine and methionine, but can
also be obtained from dietary sources such as meat, fish, and dairy products.
L-Carnitine has been widely used as a dietary supplement due to its potential benefits in improving
exercise performance, increasing fat burning, and promoting weight loss. It has also been investigated
for its potential therapeutic effects in various medical conditions such as cardiovascular diseases,
liver diseases, and neurological disorders.
From a pharmaceutical perspective, L-Carnitine is used as an important ingredient in a number of drugs
for treating various diseases. For example, it is used in the treatment of primary and secondary
carnitine deficiencies, chronic heart failure, and peripheral arterial disease.
The market demand for L-Carnitine has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by the growing
awareness of its health benefits and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases. According to a report by
MarketsandMarkets, the global market for L-Carnitine is expected to reach USD 202.3 million by 2025,
with a CAGR of 4.5% during the forecast period.
As a chemical product, L-Carnitine is mainly produced through chemical synthesis or microbial
fermentation processes. The production process involves the use of various raw materials, including
lysine, methionine, and trimethylamine. The quality and purity of L-Carnitine are critical to its
efficacy and safety as a pharmaceutical ingredient.
In terms of the supply chain, L-Carnitine is typically supplied by chemical manufacturers to
pharmaceutical companies or dietary supplement manufacturers. The price of L-Carnitine can be affected
by various factors, such as the availability of raw materials, production costs, and market
demand.
In conclusion, L-Carnitine is a versatile amino acid with a range of potential health benefits and
pharmaceutical applications. Its market demand is expected to continue growing, driven by the increasing
prevalence of chronic diseases and the growing awareness of its health benefits. As a chemical product,
the quality and purity of L-Carnitine are critical to its efficacy and safety, and its production
involves a complex supply chain that involves various upstream and downstream players in the
pharmaceutical and dietary supplement industries.