
| N/A |
| Packing | |
|---|---|
| Storage | Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years;In solvent -80°C 6 months, -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping | Room temperature in continental US; may vary elsewhere |
Tel: 0086-25-52397805
Email: info@alchemist-chem.com

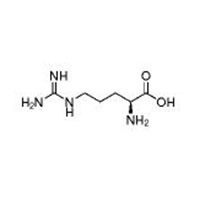
| Common Names | L(+)-Arginine | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure |  |
||
| CAS No. | 74-79-3 | Boiling Point (℃) | 367.6±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Weight | 174.201 | Melting Point (℃) | 222 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Vapor Specific Gravity | N/A |
| Molecular Formula | C6H14N4O2 | Flash Point (℃) | 176.1±30.7 °C |
| Solubility | N/A | Autoignition Temperature (℃) | N/A |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | T+:Very toxic | ||
| Safety Phrases | S1-S28-S45 | ||
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport | ||
| WGK Germany | 3 | ||
| SYMPTOMS | PREVENTION | FIRST AID | |
| Inhalation | Cough. Sore throat. | Use local exhaust or breathing protection. | Fresh air, rest. |
| Skin | Redness. Burning sensation. Itching. | Protective gloves. | Remove contaminated clothes. Rinse and then wash skin with water and soap. |
| Eyes | Redness. Pain. | Wear safety goggles. | First rinse with plenty of water for several minutes (remove contact lenses if easily possible), then refer for medical attention. |
| Ingestion | Abdominal pain. Nausea. Vomiting. | Do not eat, drink, or smoke during work. Wash hands before eating. | Rinse mouth. Induce vomiting (ONLY IN CONSCIOUS PERSONS!). Refer for medical attention. |
| Description | L-Arginine is the nitrogen donor for synthesis of nitric oxide, a potent vasodilator that is deficient during times of sickle cell crisis.Target: OthersL-Arginine is an α-amino acid. It was first isolated in 1886. The L-form is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids. At the level of molecular genetics, in the structure of the messenger ribonucleic acid mRNA, CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG, are the triplets of nucleotide bases or codons that code for arginine during protein synthesis. In mammals, arginine is classified as a semiessential or conditionally essential amino acid, depending on the developmental stage and health status of the individual.L-Arginine is associated with a decrease in cardiac index while stroke index is maintained in patients with severe sepsis. Resolution of shock at 72 hours is achieved by 40% and 24% of the patients in the L-Arginine and placebo cohorts, respectively. L-Arginine (450 mg/kg during a 15-minute period) amplifies and sustains the hyperemia (38%) and increases absolute brain blood flow after eNOS upregulation by chronic simvastatin treatment (2 mg/kg subcutaneously, daily for 14 days) in SV-129 mice. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Target | Human Endogenous Metabolite | ||
| In Vitro | DL-Lysine (Lys) is a high affinity, basic amino acid substrate for amino acid transporter b0,+ with Km value ranging from 100-400 μM[1]. | ||
| References | [1]. Tapiero H, et al. I. Arginine. Biomed Pharmacother. 2002 Nov;56(9):439-45. [2]. Bakker J, et al. Administration of the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor NG-methyl-L-arginine hydrochloride (546C88) by intravenous infusion for up to 72 hours can promote the resolution of shock in patients with severe sepsis: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter study (study no. 144-002). Crit Care Med. 2004 Jan;32(1):1-12. [3]. Yamada M, et al. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase-dependent cerebral blood flow augmentation by L-arginine after chronic statin treatment. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000 Apr;20(4):709-17. | ||