
| N/A |
| Packing | |
|---|---|
| Storage | Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years;In solvent -80°C 6 months, -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping | Room temperature in continental US; may vary elsewhere |
Tel: 0086-25-52397805
Email: info@alchemist-chem.com

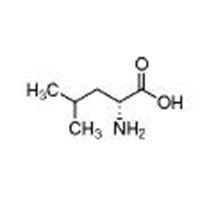
| Common Names | D-Leucine | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure |  |
||
| CAS No. | 328-38-1 | Boiling Point (℃) | 225.8±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Weight | 131.173 | Melting Point (℃) | > 300ºC |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Vapor Specific Gravity | N/A |
| Molecular Formula | C6H13NO2 | Flash Point (℃) | 90.3±22.6 °C |
| Solubility | N/A | Autoignition Temperature (℃) | N/A |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | T+:Very toxic | ||
| Safety Phrases | S1-S28-S45 | ||
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport | ||
| WGK Germany | 3 | ||
| SYMPTOMS | PREVENTION | FIRST AID | |
| Inhalation | Cough. Sore throat. | Use local exhaust or breathing protection. | Fresh air, rest. |
| Skin | Redness. Burning sensation. Itching. | Protective gloves. | Remove contaminated clothes. Rinse and then wash skin with water and soap. |
| Eyes | Redness. Pain. | Wear safety goggles. | First rinse with plenty of water for several minutes (remove contact lenses if easily possible), then refer for medical attention. |
| Ingestion | Abdominal pain. Nausea. Vomiting. | Do not eat, drink, or smoke during work. Wash hands before eating. | Rinse mouth. Induce vomiting (ONLY IN CONSCIOUS PERSONS!). Refer for medical attention. |
| Description | D-Leucine is a more potent anti-seizure agent than L-leucine. D-leucine potently terminates seizures even after the onset of seizure activity. D-leucine, but not L-leucine, reduces long-term potentiation but had no effect on basal synaptic transmission in vitro[1]. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Target | Human Endogenous Metabolite | ||
| In Vitro | In a screen of candidate neuronal receptors, D-leucine failed to compete for binding by cognate ligands, potentially suggesting a novel target. Even at low doses, D-leucine suppressed ongoing seizures at least as effectively as diazepam but without sedative effects. These studies raise the possibility that D-leucine may represent a new class of anti-seizure agents, and that D-leucine may have a previously unknown function in eukaryotes[1]. | ||
| References | [1]. Xiaoyu Cao, et al. Combination of PARP Inhibitor and Temozolomide to Suppress Chordoma Progression. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019 Aug;97(8):1183-1193 | ||