
| N/A |
| Packing | |
|---|---|
| Storage | Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years;In solvent -80°C 6 months, -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping | Room temperature in continental US; may vary elsewhere |
Tel: 0086-25-52397805
Email: info@alchemist-chem.com

| Common Names | D-Glutamic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|
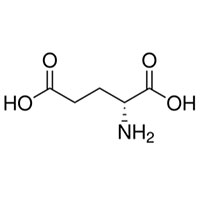
| Structure |  |
||
| CAS No. | 6893-26-1 | Boiling Point (℃) | 333.8±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Weight | 147.129 | Melting Point (℃) | 200-202ºC |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Vapor Specific Gravity | N/A |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9NO4 | Flash Point (℃) | 155.7±25.1 °C |
| Solubility | N/A | Autoignition Temperature (℃) | N/A |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | T+:Very toxic | ||
| Safety Phrases | S1-S28-S45 | ||
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport | ||
| WGK Germany | 3 | ||
| SYMPTOMS | PREVENTION | FIRST AID | |
| Inhalation | Cough. Sore throat. | Use local exhaust or breathing protection. | Fresh air, rest. |
| Skin | Redness. Burning sensation. Itching. | Protective gloves. | Remove contaminated clothes. Rinse and then wash skin with water and soap. |
| Eyes | Redness. Pain. | Wear safety goggles. | First rinse with plenty of water for several minutes (remove contact lenses if easily possible), then refer for medical attention. |
| Ingestion | Abdominal pain. Nausea. Vomiting. | Do not eat, drink, or smoke during work. Wash hands before eating. | Rinse mouth. Induce vomiting (ONLY IN CONSCIOUS PERSONS!). Refer for medical attention. |

| Description | D-glutamic acid, an enantiomer of L- glutamic acid, is widely used in pharmaceuticals and foods. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Target | Km: 100-400 μM (amino acid transporter b0,+)[1] | ||
| In Vitro | Various d-amino acids, such as D-serine, D-aspartic acid (D-Asp), and D-glutamic acid (D-Glu) are widely found in mammals including human beings and they are now thought to be the candidates of novel physiologically active substances and/or biomarkers[1]. D-[Asp/Glu] (4 mg/mL) inhibits IgE binding (75%) to peanuts while D-Glu, D-Asp has no inhibitory effect. IgE is specific for D-[Asp/Glu] and may have the potential for removing IgE or reducing IgE binding to peanut allergens[2]. | ||
| References | [1]. Han H, et al. Changes in D-aspartic acid and D-glutamic acid levels in the tissues and
physiological fluids of mice with various D-aspartate oxidase activities. J Pharm Biomed
Anal. 2015 Dec 10;116:47-52. [2]. Chung SY, et al. IgE binding to peanut allergens is inhibited by combined D-aspartic and D-glutamic acids. Food Chem. 2015 Jan 1;166:248-53. |
||